CCSP: Security Control Frameworks
ISO 27001, ISO 27002, ISO 27017, ISO 27018, NIST (CSF, RMF), SOC2, PCI DSS
Information Security Management System (ISMS)
The goal of an ISMS is to ensure a coherent organisational approach to managing information security risks.
It’s an organisation’s overarching approach to preserve the confidentiality, integrity and availability of systems and data in use.
Various standards and frameworks exist to help organisations implement, manage, and in some cases, audit or certify the ISMS.
A Security Control Framework
A security control framework is essentially a blueprint for managing cybersecurity risks in an organisation.
It is a structured plan that outlines policies, procedures, and best practices to safeguard data, systems, and applications.
Structure and organisation
It provides a systematic approach to security, ensuring all aspects are considered.
It categorises security controls into different areas like
Access control
Data protection
Incident response
Best practices
It incorporates widely accepted security practices, helping organisations stay up-to-date with evolving threats.
It offers recommendations on how to implement controls effectively, considering industry standards and regulations.
Compliance assistance
Some frameworks align with specific regulations, aiding organisations in achieving compliance. This can be helpful for industries with strict data privacy requirements.
There are frameworks that focus on both security controls as well as the overall ISMS functions.
ISO Security Control Frameworks
ISO 27001
Description: Information Security Management Systems (ISMS)
Focus: Provides a framework for an organisation to establish, maintain, and continually improve an ISMS to manage security risks.
Achievable certification: Yes
ISO 27002
Description: Information Technology -Security Techniques, Information Security Controls
Focus: Lists a comprehensive set of information security controls that an organisation can use to implement an ISMS based on ISO 27001
Achievable certification: No (It’s a reference guide)
ISO 27017
Description: Code of practice for information security controls for cloud use
Focus: Provides specific guidance on implementing ISO 27002 controls in a cloud computing environment
Achievable certification: No (It’s a code of practice)
ISO 27018
Description: Protection of Personally Identifiable Information (PII) in public cloud as PII processors
Focus: Offers implementation guidance for protecting PII in public cloud environments based on ISO 27001 and ISO 27002
Achievable certification: No (It’s a code of practice)
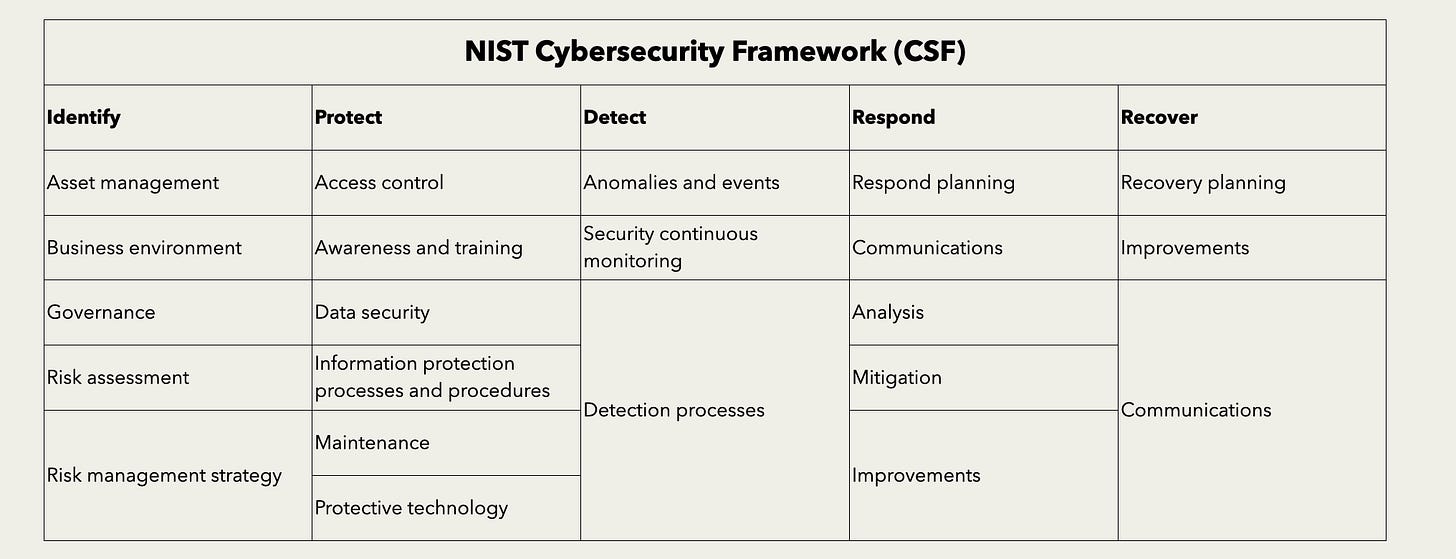
NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF)
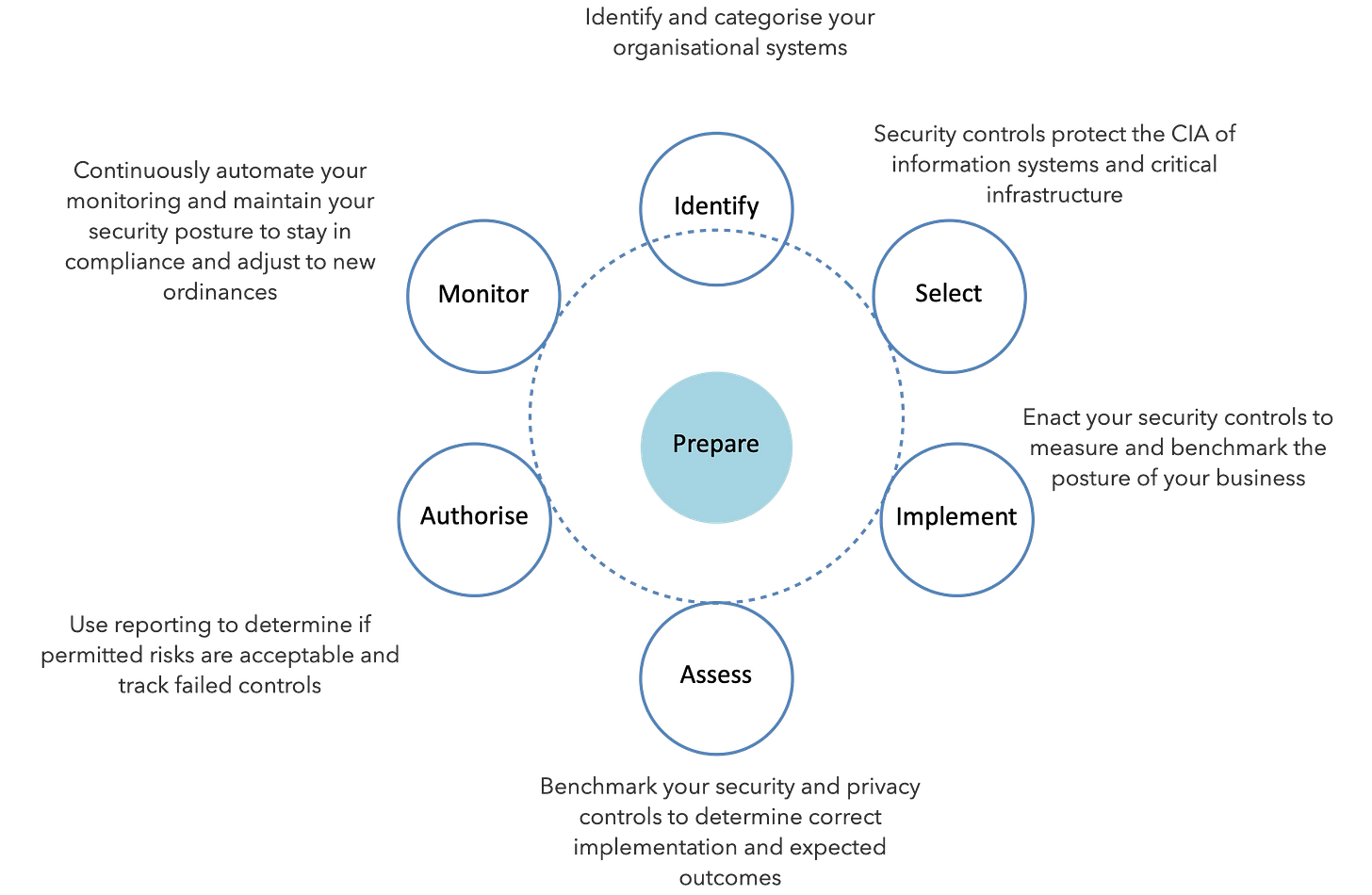
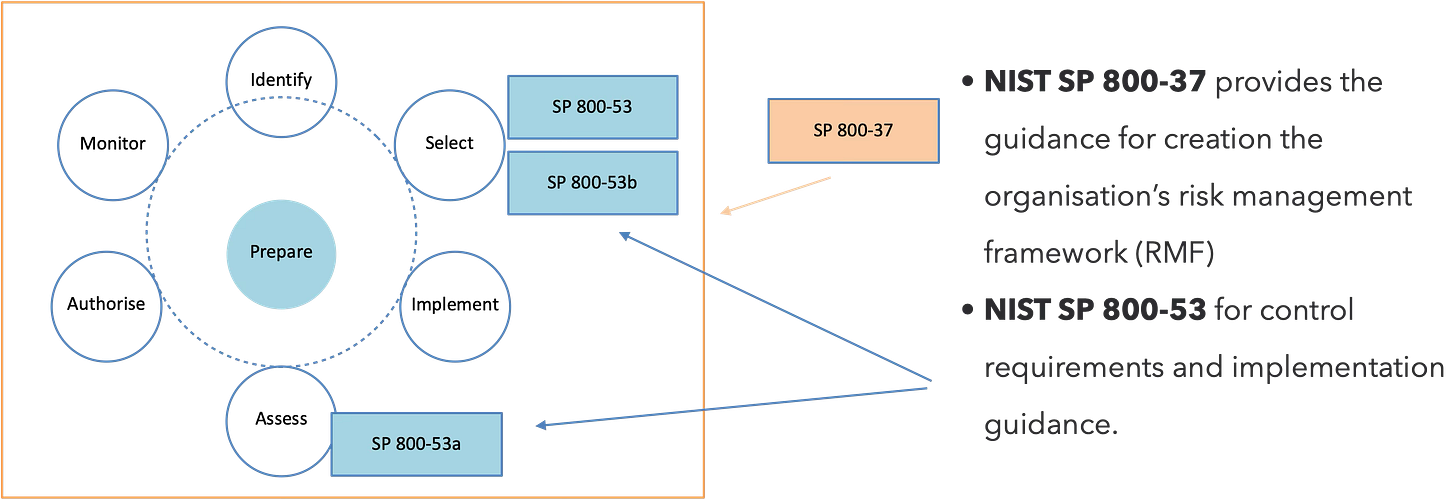
NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF)
Identify information security risks and apply adequate risk mitigations in the form of security controls.
NIST Special Publications
Service Organisation Controls (SOC 2)
The SOC 2 framework has seen wide adoption among Cloud Service Providers (CSPs)
This adoption is primarily as a result of the relatively lightweight approach it provides and the use of third-party audits; which provides increased assurance for business partners and customers.
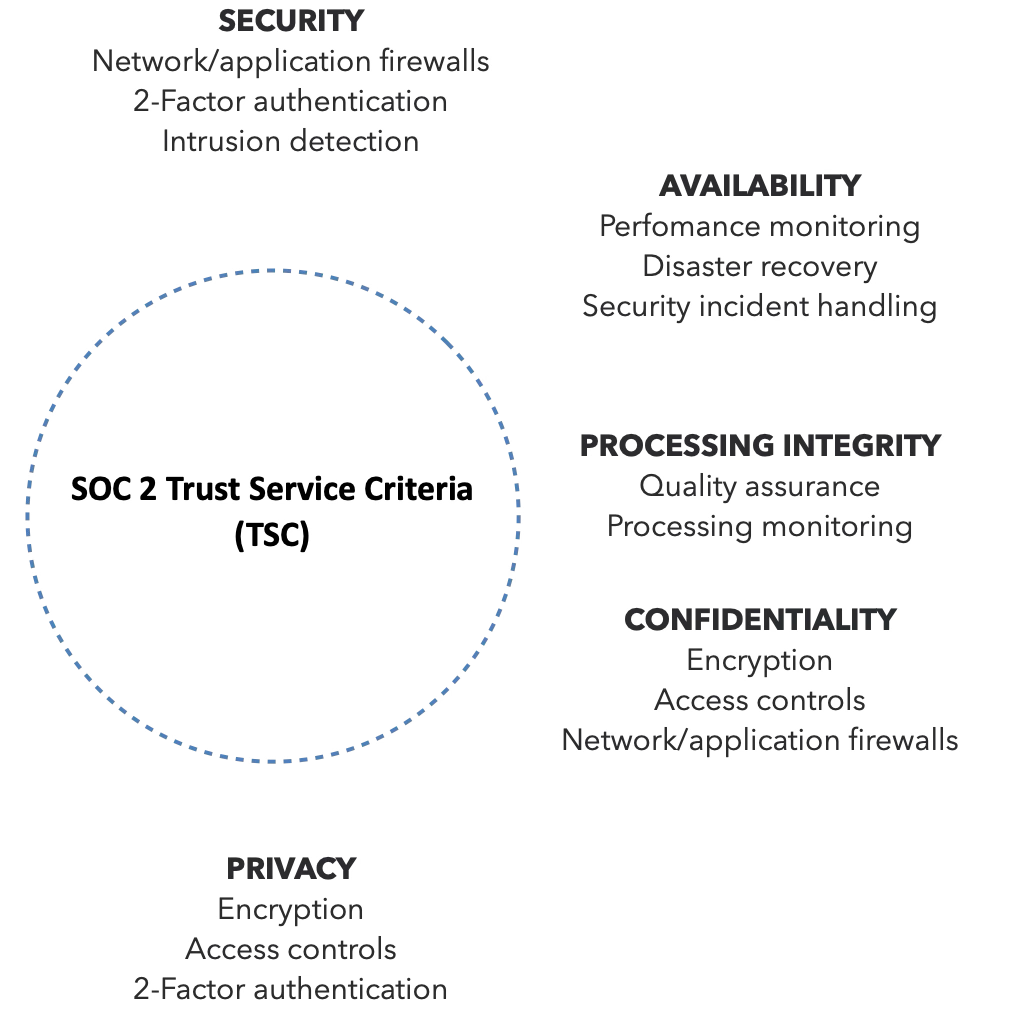
SOC 2 contains Trust Service Criteria (TSC), which cover organisational aspects including
Security
Availability
Processing integrity
Confidentiality
Privacy
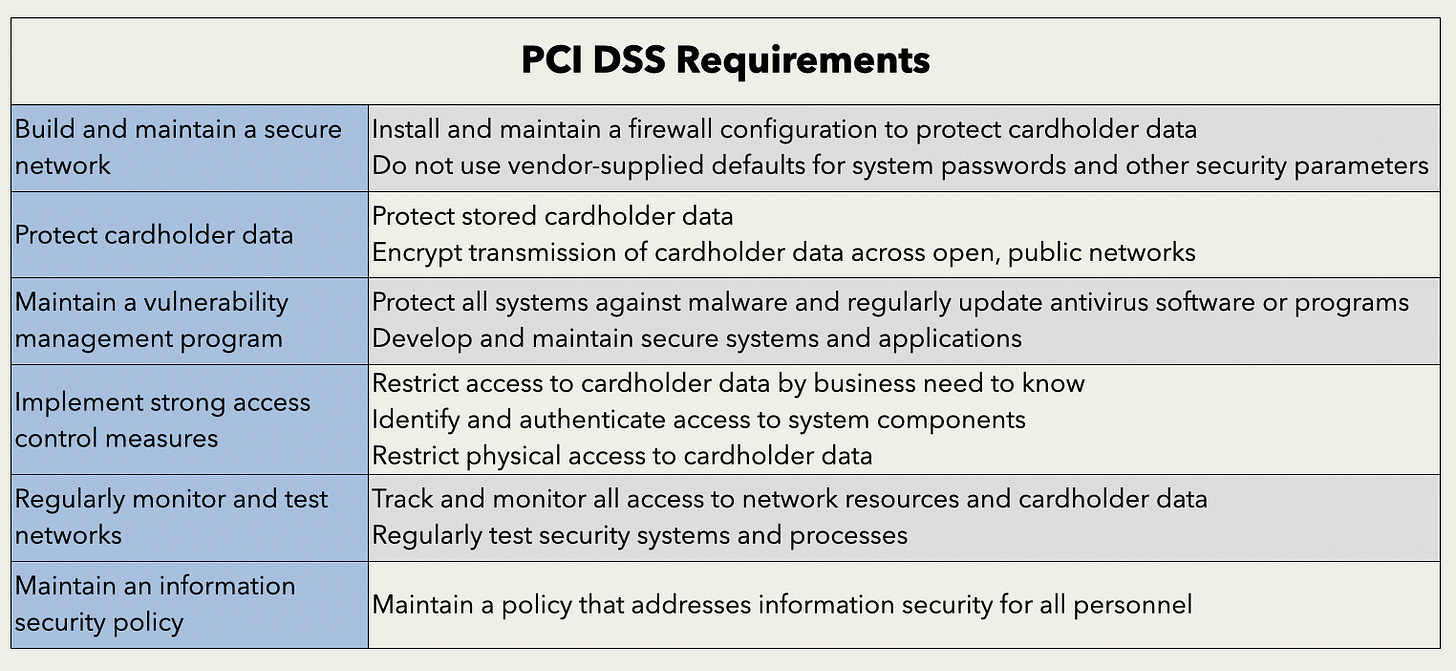
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
PCI DSS is a security control framework focused specifically on protecting cardholder data.
Defines security requirements
PCI DSS outlines a set of 12 core requirements that organisations must implement to safeguard cardholder data. These requirements cover areas like
Access control
Network security
Data encryption
Vulnerability management
Provides best practices
While not as comprehensive as broader frameworks like NIST CSF, PCI DSS incorporates best practices for securing payment card data.
Compliance focus
A core function of PCI DSS is ensuring compliance with the data security standards mandated by the payment card industry.
Organisations that handle transactions need to adhere to PCI DSS to maintain acceptance of payment cards.